Electrode Potential and Standard Electrode Potential
Electrode Potential and Standard Electrode Potential: Overview
This Topic covers sub-topics such as Electrode Potential, Standard Hydrogen Electrode, Calomel Electrode, Reference Electrodes, Measurement of EMF of a Cell, Reduction Electrode Potential and, Standard Reduction Electrode Potential
Important Questions on Electrode Potential and Standard Electrode Potential
Two half-cell reactions of an electrochemical cell are given below :
What would be the final cell potential?
A copper-silver cell is set up. The copper ion concentration in it is 0.10 M. The concentration of silver ion is not known. The cell potential measured is 0.422 V. Determine the concentration of silver ion in the cell. Given : .
An acidic solution of salt containing is electrolysed until all the copper is deposited. The electrolysis is continued for seven more minutes with the volume of solution kept at 100 mL and the current at 1.2 amp. The volume of gases evolved at NTP during the entire electrolysis:
A solution containing one mole per litre of each is being electrolysed by using inert electrodes. The values of standard electrode potentials in volts are :
With increasing voltage, the sequence of deposition of metals on the cathode will be :
The equilibrium constant for the reaction, would be, if the standard reduction potentials in acidic conditions are 0.77 V and 0.54 V respectively for couple.
The standard potential of the following cell is 0.23 V at and 0.21 V at .
(ii) Calculate for the cell reaction by assuming that these quantities remain unchanged in the range .
(iii) Calculate the solubility of AgCl in water at .
Given: The standard reduction potential of the couple is 0.80 V at .
A standard hydrogen electrode has zero electrode potential because
The emf of the cell:
at is Then the value of equilibrium constant for the cell reaction is:
Standard electrode potential data are useful for understanding the suitability of an oxidant in a redox titration. Some half cell reactions and their standard potentials are given below :
Identify the only incorrect statement regarding the quantitative estimation of aqueous
When the samples of copper with zinc impurity is to be purified by electrolysis, the appropriate electrodes are –
Calculate Reduction Potential of hydrogen electrode at which is prepared with the help of aq. solution of acetic acid with conc at atm pressure
The incorrect statements from the following is:
A. The electrical work that a reaction can perform at constant pressure and temperature is equal to the reaction Gibbs energy.
B. is dependent on the pressure.
C.
D. A cell is operating reversibly if the cell potential is exactly balanced by an opposing source of potential difference.
Which of the following is oxidised by oxygen in acidic medium?
For the galvanic cell : , Calculate the EMF generated and assign correct polarity to each electrode for a spontaneous process after taking into account the cell reaction at .
One of the most common cells that's been used in our daily life is Duracell, also known as an alkaline cell. The image below shows the internal structure of a Duracell.
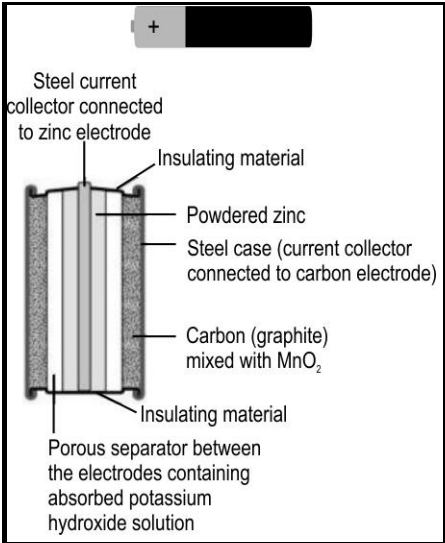
This cell uses a zinc half-cell and another half-cell containing a carbon (graphite) electrode in contact of moist manganese oxide. Given that the electrode potential for
Which of the two will be the positive electrode and why?
One of the most common cells that's been used in our daily life is Duracell, also known as an alkaline cell. The image below shows the internal structure of a Duracell.
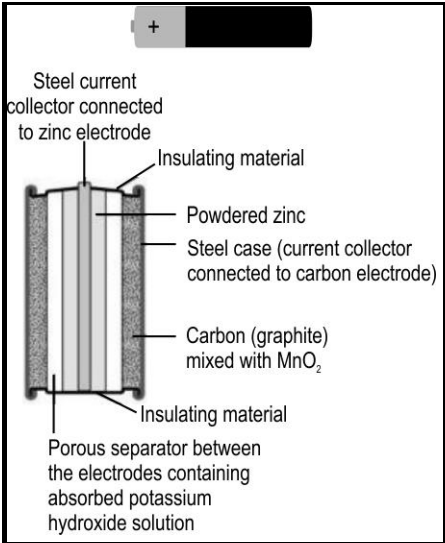
This cell uses a zinc half-cell and another half-cell containing a carbon (graphite) electrode in contact of moist manganese oxide. Given that the electrode potential for
Calculate the overall cell potential.
What is Latimer diagram ?
Which of the following facts is not true?
and are added to a solution containing each of and . What reaction will take place? Given that the reduction potentials of and are and, respectively.
When silver electrode having reduction potential is connected to to make a cell, will it act as anode or cathode?
